New Study Showcases MP-SPR for Protein Thiol Analysis
A recent study by Souza et al. (Langmuir, 2024) demonstrates the potential of Multi-Parametric Surface Plasmon Resonance (MP-SPR) in quantifying thiol groups in proteins. By adapting Ellman’s assay for surface-based analysis, the researchers immobilized human cofilin-1 (CFL-1) on gold-coated sensors and successfully quantified its thiol groups. The study highlights the precision of MP-SPR in measuring molecular interactions and surface coverage, providing a valuable approach for characterizing thiol-containing proteins. This approach provides a novel surface-based tool for studying thiol-containing proteins, offering a reliable technique for future research in protein interactions, drug discovery and neurodegenerative disease studies.
Detailed Study Overview:
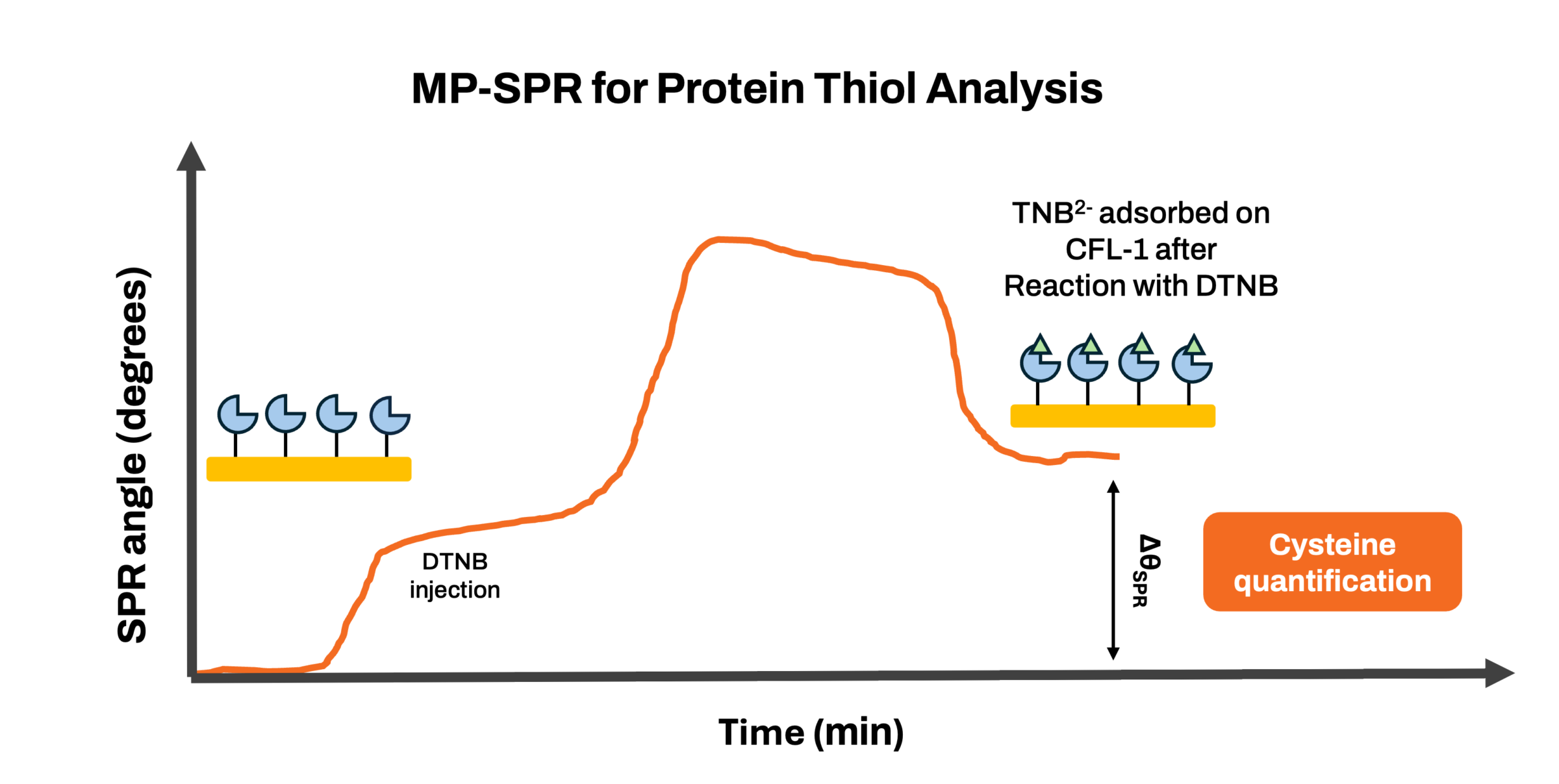
This study adapts Ellman’s assay (Figure 1) for thiol quantification in human cofilin-1 (CFL-1) using MP-SPR. CFL-1 was immobilized on gold-coated sensors via a 3-mercaptopropionic acid (MPA) self-assembled monolayer, and its thiol groups reacted with Ellman’s reagent (DTNB), forming 2-nitro-5-thiobenzoate (TNB2−). Surface coverage (Γ) was calculated using the de Feijter equation. A correction factor adjusted for molecular weight and stoichiometry, ensuring accuracy in quantifying thiols. CFL-1 showed a surface coverage of 6.5 ± 0.6 pmol/cm², while TNB2− coverage was 26.5 pmol/cm², yielding a TNB2− : CFL-1 ratio of ~4.1, consistent with CFL-1’s four cysteine residues. A control experiment with oxidized CFL-1 confirmed the specificity of this method.
You can find the original publication here: Souza et al., Langmuir 2024.